Symptoms of Excess Sugar in the Human Body
Without a doubt, sugar is very addictive, in fact we find it in numerous foods. Even no one can resist a delicious dessert or chocolate, although it is true that consuming these delicacies from time to time is not bad, the problem is the quantity. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the symptoms of excess sugar in the human body.
The issue is the problems that come in the long term, so it is necessary to take urgent measures. In this regard, the World Health Organization recommends that we reduce the consumption of sugars throughout life, not only for adults but also for children.
Precisely, this is due to not suffering the consequences later in life. Therefore, we must get used to checking food labels to make sure of their sugar content. Since we know well that sugar is found not only in desserts, but also in bread, cereals, dressings, etc.
More importantly, we must learn to detect our body’s signals and what they tell us about our health. How many times has the presence of pimples been linked to acne, as well as headache due to excess sugar and many other diseases due to excess sugar:
The excess sugar it produces
As expected, excessive sugar consumption will have negative consequences. The following symptoms of excess sugar in the human body are listed below:
- Weight gain:
There’s a simple and obvious rule to keep in mind: the body converts sugar into energy. Therefore, if we increase our sugar consumption, it must be compensated with physical activity. If this does not happen, then the body saves the excess in the form of fat to use later.
If you notice an increase in your weight, especially in the abdominal area, and you haven’t changed your exercise habits, it could be a sign that you’re consuming more sugar than your body can handle. This is a key time to reduce your intake and increase your physical activity to avoid major complications, such as obesity or heart problems.
- Tiredness and lack of energy:
It’s common to hear that sugar gives us an energy boost, but high consumption can backfire. When consuming something very sweet, glucose and insulin levels skyrocket.
The problem is that this rapid increase is followed by a drop in energy, which leads to tiredness and often more hunger. If after eating something sweet you feel exhausted or experience a “roller coaster” of energy and fatigue, it’s a clear indication that too much sugar is affecting your energy levels. To avoid these peaks and lows, opt for foods with slow-absorbing carbohydrates, such as oatmeal or whole fruits.
- Urgency for something sweet:
A sudden craving for sweets can be a sign of sugar addiction. This addiction is comparable to that of substances such as cocaine, as sugar activates the same pleasure circuits in the brain.
If you find that you constantly feel an urgent need to eat something sweet, even after you’ve eaten, you’re likely developing a sugar addiction. This is a sign that your body has become accustomed to high doses of sugar and relies on them to produce dopamine. In this case, gradually reducing your consumption of sweets can help you overcome the addiction.
- Constant illnesses:
A clear example of this effect is the appearance of frequent colds or flu. This can happen when nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits and vegetables, are replaced by sugary products such as cookies or candy.
If you get sick frequently and notice that you have colds more often than usual, it could be a red flag that excess sugar is weakening your immune system. Excessive sugar intake can affect your cells’ ability to fight infection, so it’s essential to increase your intake of foods rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, and cut back on sweets.
- Increased resistance to sweetness:
Constant consumption of sugar can damage the taste buds, reducing the ability to perceive sweet tastes. Studies conducted in Great Britain show that people with obesity tend to prefer foods that are high in sugar, and over time, their sensitivity to sweetness decreases.
If you find that you need to add more sugar to your coffee or that sweets don’t taste as intense as they used to, it’s a sign that your body is developing a resistance to sweetness. This can lead to a vicious cycle where you consume more sugar than necessary, aggravating the health problems associated with its excess. Reducing the amount of sugar you consume can help restore your sensitivity to flavors.
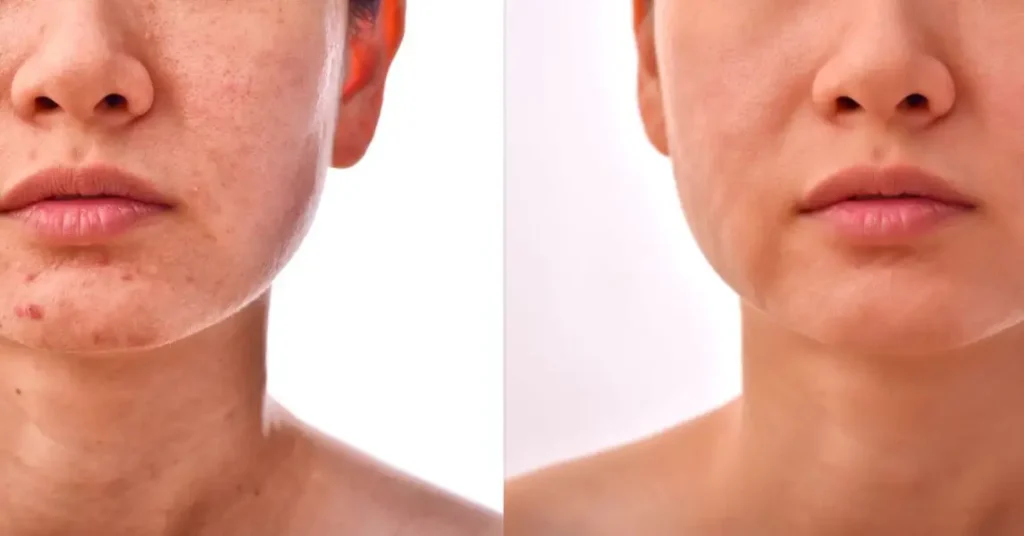
- Acne:
Acne, often related to chocolate, may have more to do with excess sugar. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as sweets, raise insulin levels, which in turn stimulates the sebaceous glands and generates inflammation in the skin.
If you notice an increase in the appearance of acne, especially after consuming sugary products, it is likely that your skin is reacting to the excess insulin in your body. Reducing your intake of foods high in sugar and opting for a diet low in refined carbohydrates can significantly improve the health of your skin.
- Cardiovascular problems:
Excessive sugar consumption is also linked to an increased risk of heart disease. This is because high blood sugar contributes to chronic inflammation and increased triglyceride levels, which negatively affects the cardiovascular system.
If you’ve noticed that you’re feeling more fatigued after physical activities that you used to do without problems, or if your doctor has noticed an increase in your triglyceride levels, it could be a sign that excess sugar is affecting your heart health. Incorporating more foods rich in fiber and healthy fats, and reducing added sugars, can help improve your cardiovascular health.
- Dental problems:
Sugar is one of the main causes of tooth decay and other dental problems. The bacteria present in the mouth use sugar as an energy source, producing acids that damage tooth enamel.
If you notice that you’ve had more cavities or that your visits to the dentist are more frequent, it’s a clear sign that your sugar intake is harming your oral health. It is essential to reduce sugar and maintain good dental hygiene to avoid more serious problems, such as infections or tooth loss.
- Metabolic problems:
Too much sugar can also contribute to the development of insulin resistance, which can lead to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes. When the body is exposed to elevated glucose levels on a consistent basis, its ability to regulate blood sugar is impaired, increasing the risk of developing this chronic disease.
If you’ve noticed that you’re constantly feeling thirsty, need to urinate more often, or are experiencing extreme fatigue, these could be signs that you’re developing insulin resistance. It’s important to see a doctor and make dietary changes, such as reducing your intake of refined sugars, to prevent further complications.
10. Mood swings and anxiety:
Excessive sugar consumption can affect the chemical balance of the brain, especially levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood. Experiencing sudden spikes and drops in glucose levels can trigger mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
If you notice that you feel more nervous or anxious after consuming sweets, or experience frequent emotional fluctuations, it could be a sign that excess sugar is affecting your mental health. To maintain a stable mood, it is advisable to reduce your intake of sugary foods and opt for a balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
How to get rid of excess sugar in the body
We must be very attentive to all the signs or symptoms that we may reflect, it is important to review and improve the habits of how we are eating. Basically, we have to lower the dose of sugar we consume, fortunately today there are countless options to replace sugar.
A recommendation to follow is to read the label of the foods we are going to consume well, it is essential to monitor the amount of sugars.
As well as, consult with our doctor to perform studies or blood tests to detect any adverse effect of sugar in our body.
👉 Follow our page, like 👍, and share this post. Every click can make a difference—perhaps saving your own life or that of a loved one.