03.03.2025
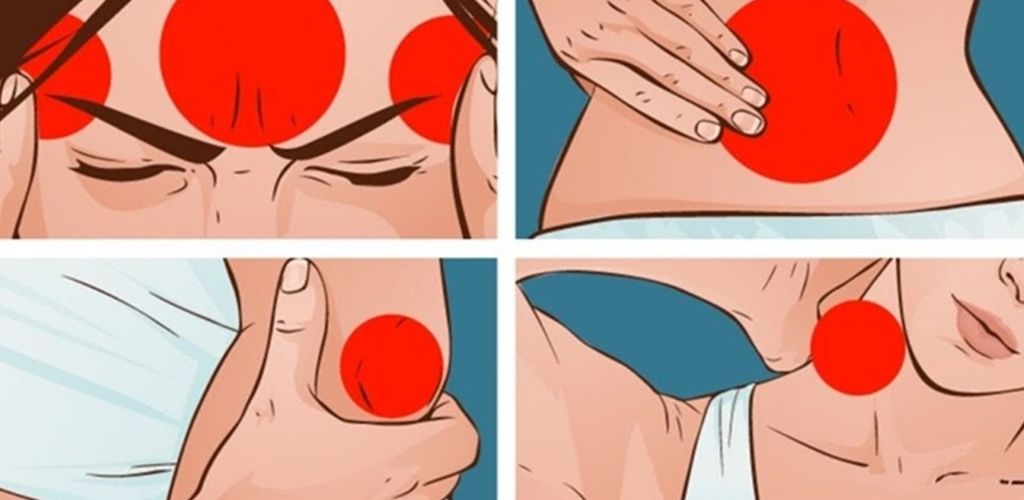
Every ache in our body is due to nerves!😲👆There are also such pains in the body that are due to nerves, emotions, and stress!🙏7 most common examples:
You’re right to highlight the significant role that nerves, emotions, and stress play in physical pain. While not every ache is solely due to nerves, the nervous system is intricately connected to our experience of pain, and psychological factors can definitely amplify or even generate physical discomfort.
Here are 7 common examples of how nerves, emotions, and stress can manifest as physical pain:
- Tension Headaches:
- Stress and anxiety often lead to muscle tension in the neck and scalp, resulting in tension headaches.
- The nervous system’s response to stress triggers muscle contractions, causing pain.
- Muscle Tension and Back Pain:
- Chronic stress can cause muscles to remain tense, particularly in the back and shoulders.
- This chronic tension can lead to pain, stiffness, and even muscle spasms.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- The gut-brain connection is strong. Stress and anxiety can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system.
- This can lead to abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
- Chest Pain (Non-Cardiac):
- Panic attacks and anxiety can cause chest tightness and pain that mimics heart problems.
- Hyperventilation, a common symptom of anxiety, can also cause chest pain.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Pain:
- Stress can lead to teeth grinding and jaw clenching, which can cause pain in the TMJ, the joint that connects the jaw to the skull.
- Fibromyalgia:
- This chronic condition is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
- It’s believed that stress and emotional trauma can trigger or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms.
- The way the brain processes pain signals is thought to be altered in people with fibromyalgia.
- Pelvic Pain:
- Chronic pelvic pain can be linked to stress, anxiety, and emotional trauma.
- Muscle tension in the pelvic floor can contribute to pain.
How Nerves, Emotions, and Stress Contribute:
- Nervous System Response: Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can 1 increase muscle tension and pain sensitivity.
- Brain-Body Connection: The brain and body are constantly communicating. Emotional states can influence physical sensations, and vice versa.
- Pain Perception: Stress and anxiety can lower the pain threshold, making individuals more sensitive to pain.
- Muscle Tension: Chronic stress often results in chronic muscle tension.
What Can Help:
- Stress Management Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapies can help address the emotional and psychological factors that contribute to pain.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and muscle tension.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritize getting enough sleep.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can support overall well-being.
- Consult a Doctor: If you experience persistent pain, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.